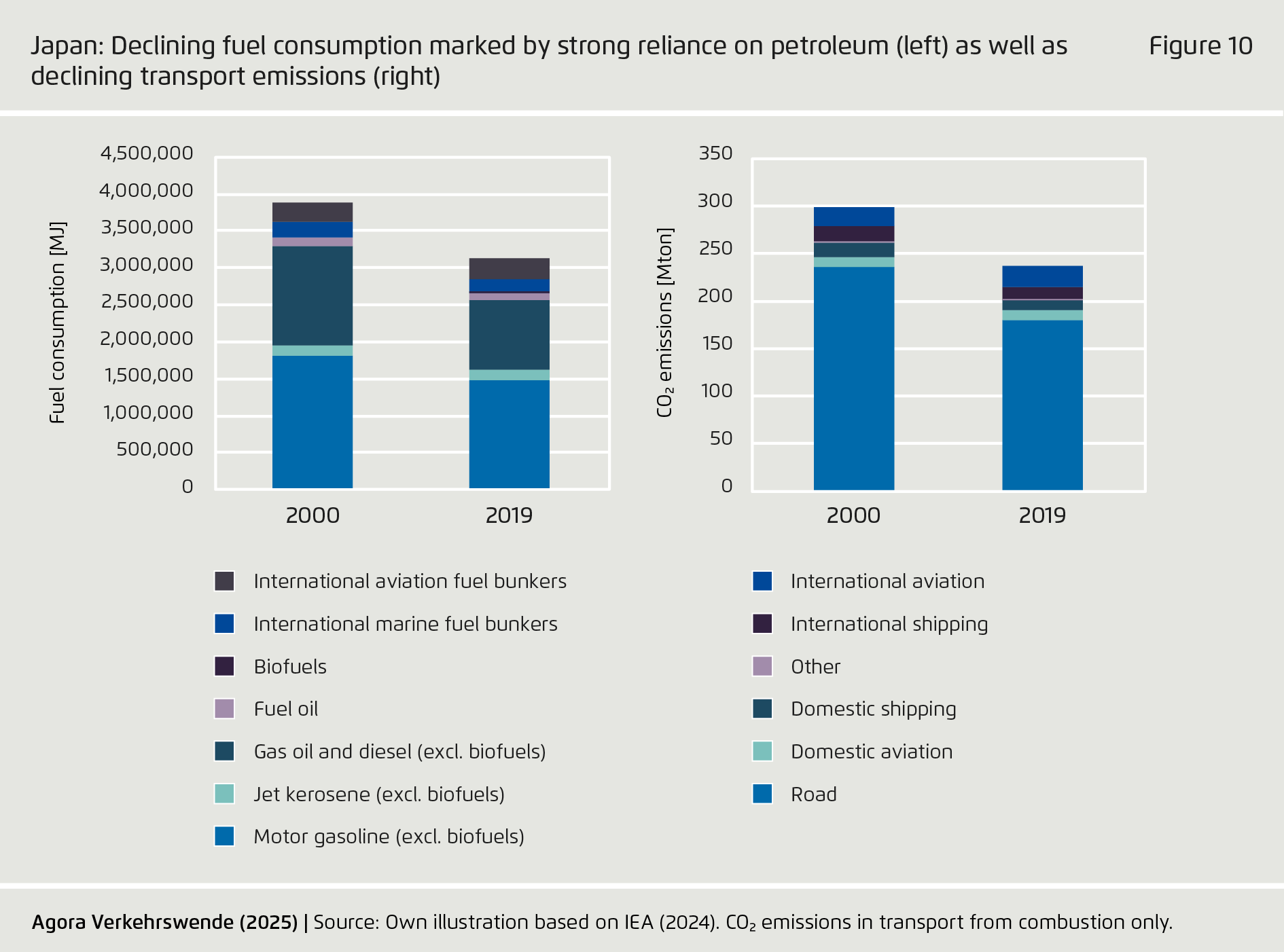
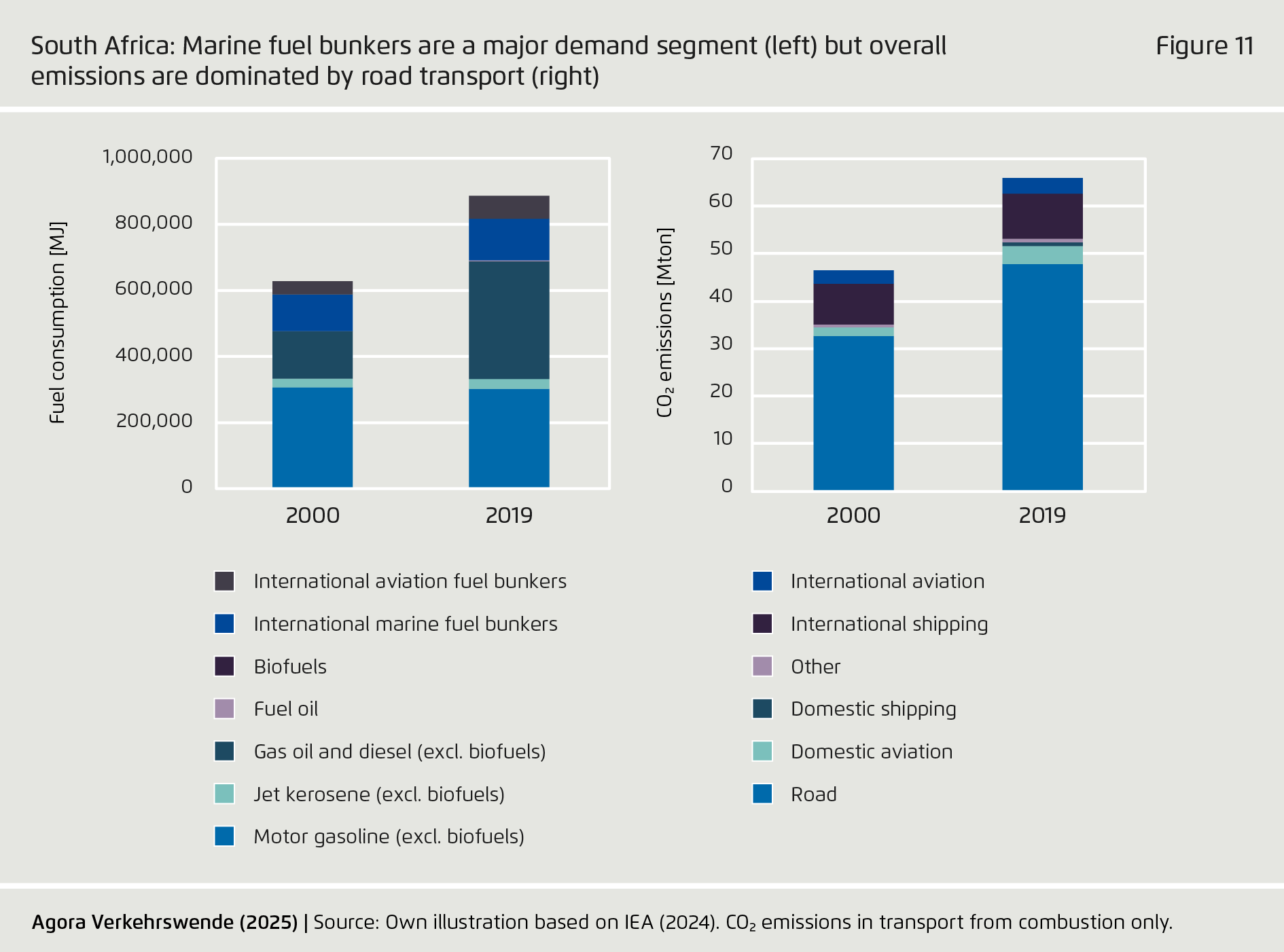
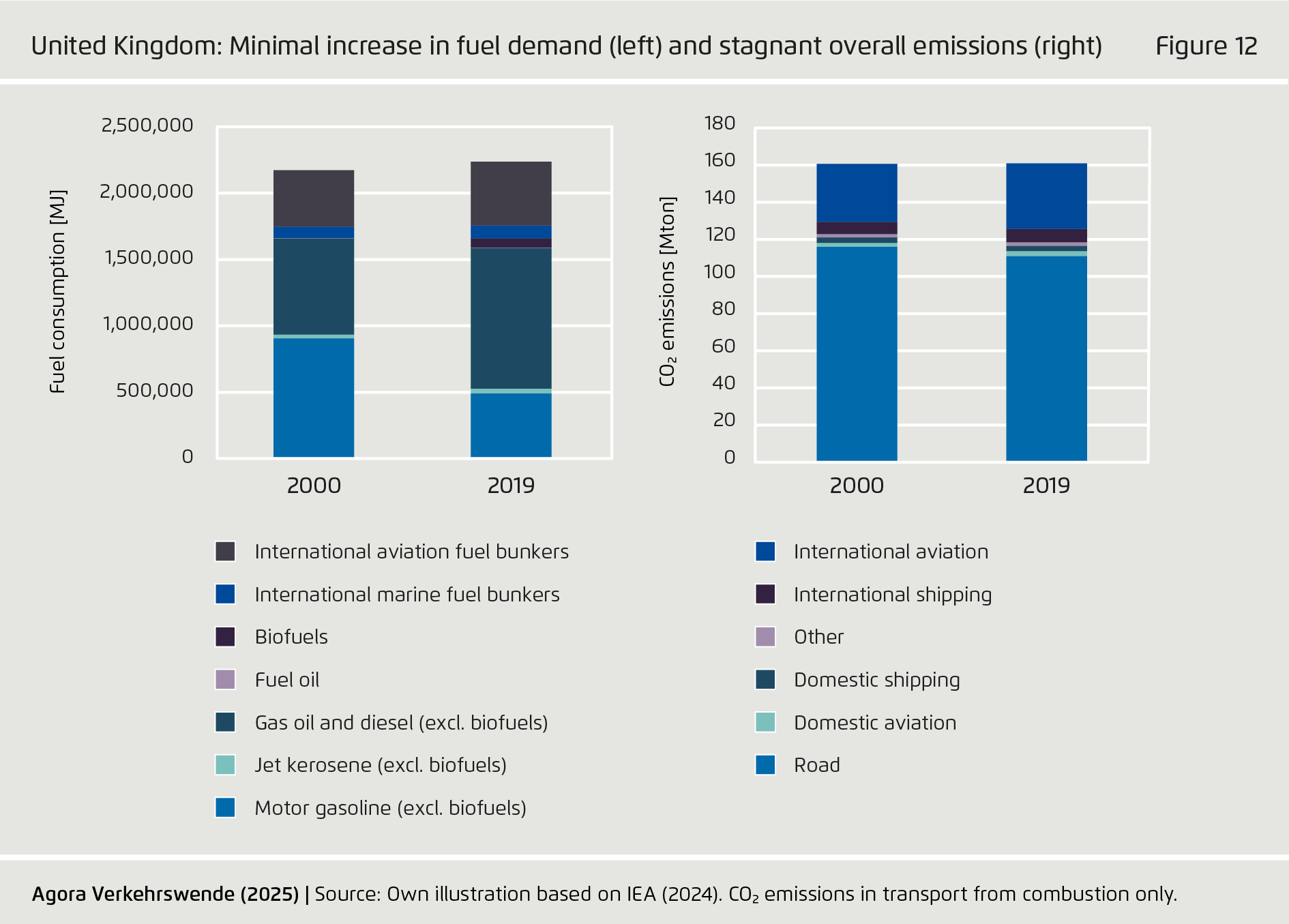
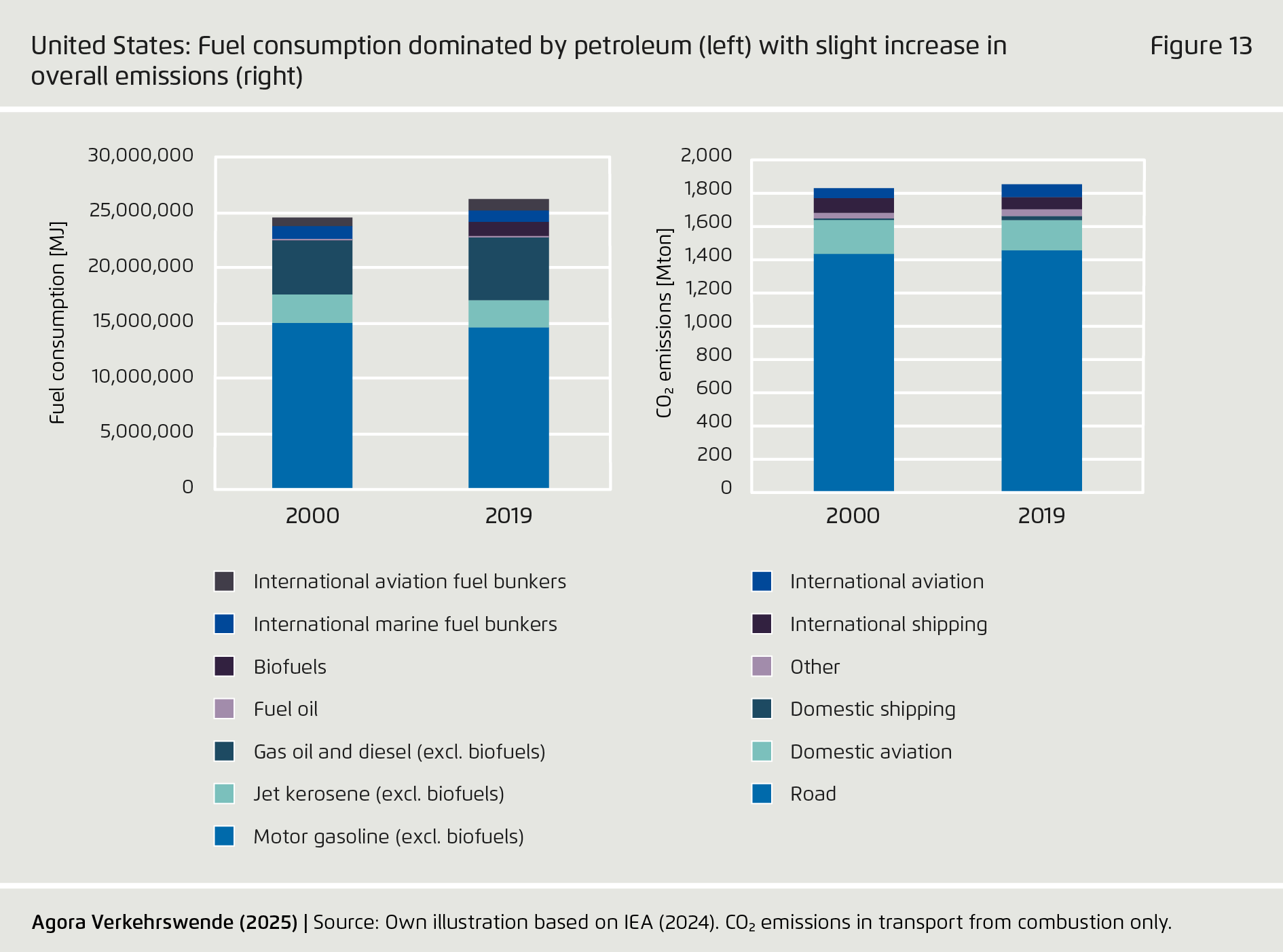
-
The slow pace of market ramp-up for PtX fuels is jeopardizing emission reduction targets.
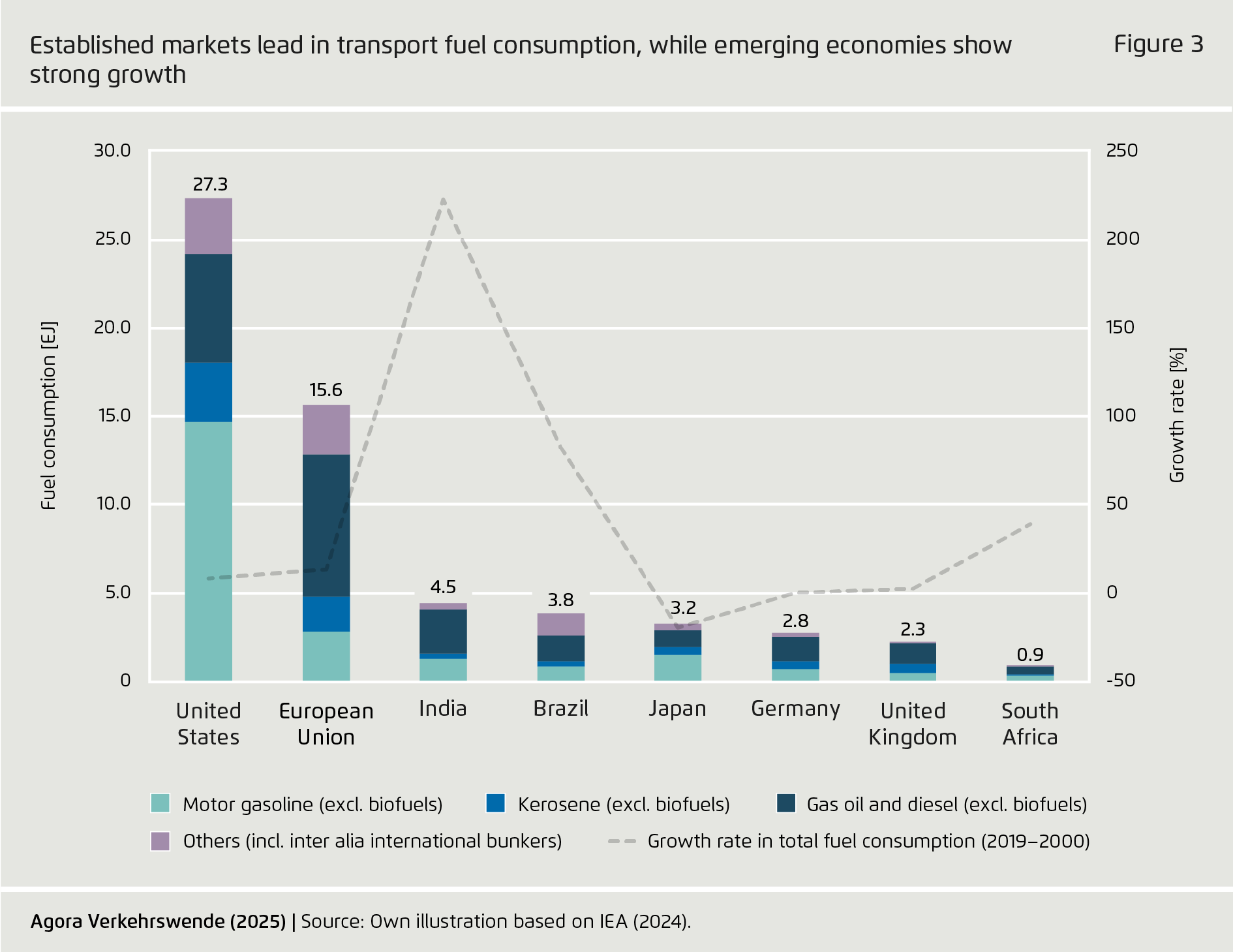
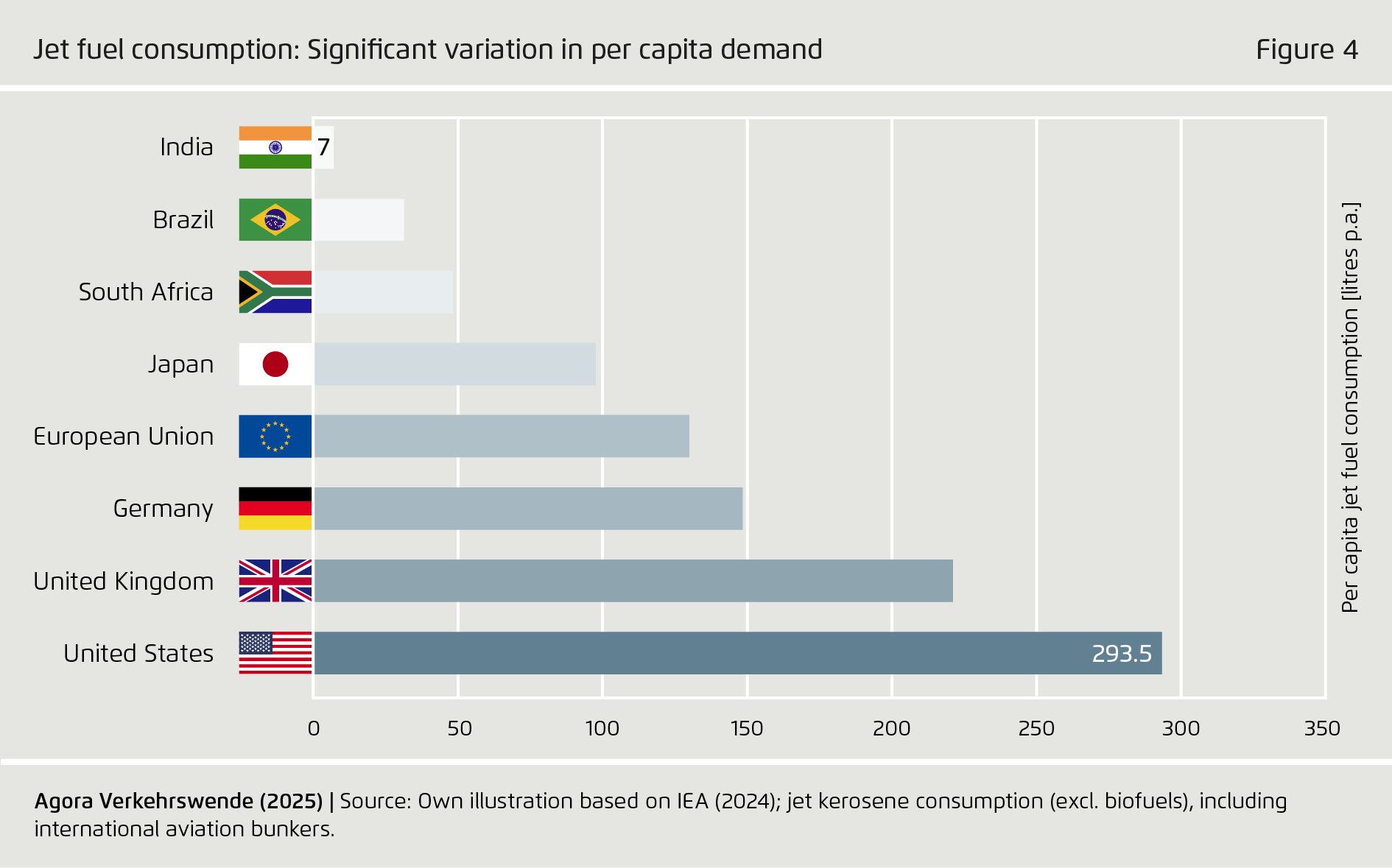
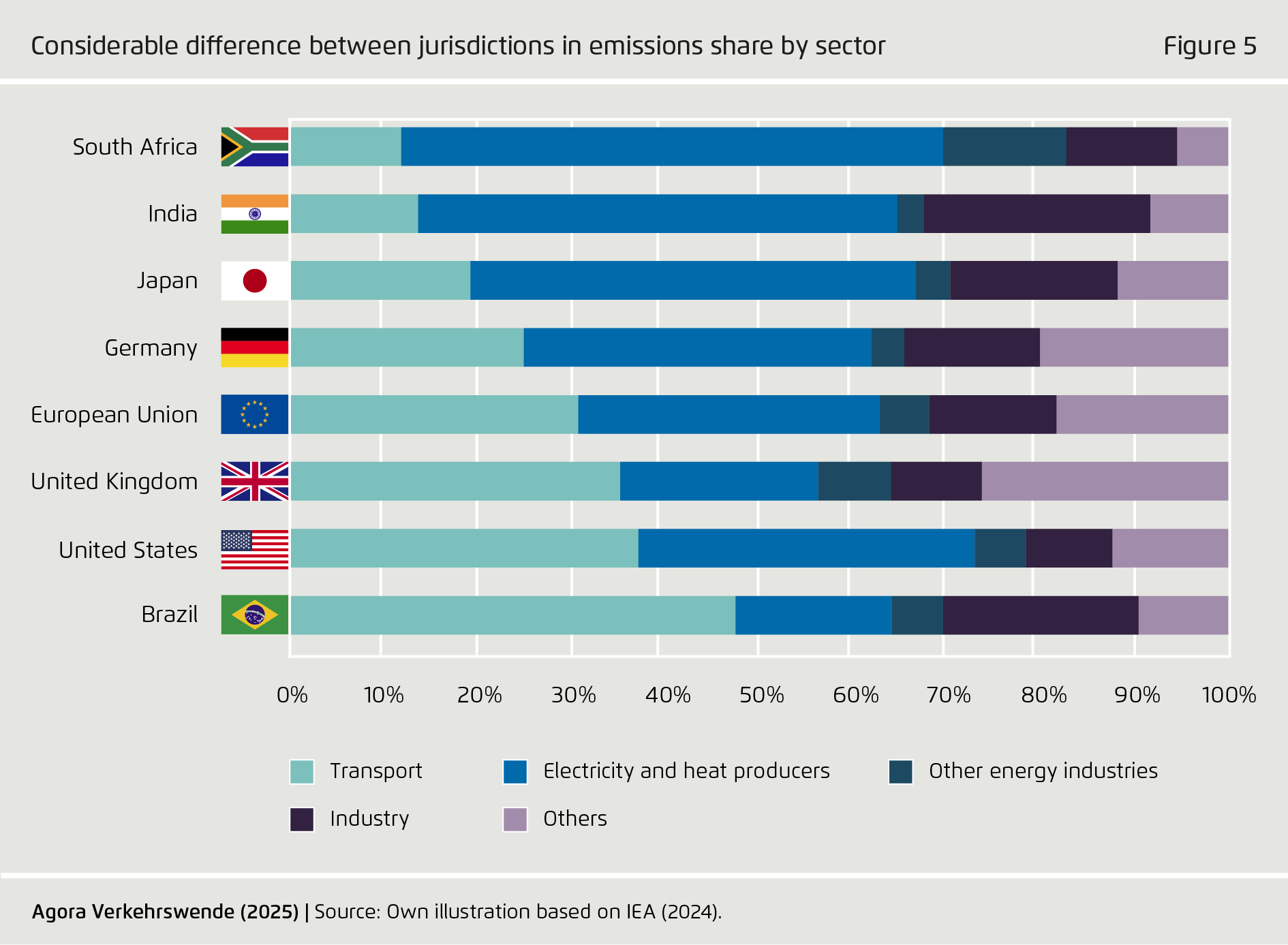
Lack of progress particularly threatens climate protection efforts in international aviation and shipping, as these transport subsectors lack electrification options. While various countries plan to build largescale PtX fuel production facilities, projects have been struggling to reach final investment decisions. Cost-effective PtX production at scale has not yet taken place. Given projected transport sector growth, particularly in aviation and shipping, PtX deployment needs to take place on the widest possible basis, including in low- and middle-income countries.
-
The price gap between PtX fuels and conventional alternatives is the key challenge.
This price gap significantly impairs growth in both supply and demand. Offtakers such as airlines and vessel operators are used to purchasing fuels in spot markets at usually cheap prices; they are therefore reluctant to enter into long-term purchase agreements for PtX. Meanwhile, PtX fuel producers must demonstrate long-term agreements with buyers in order to attract investment capital at reasonable cost-of-capital rates. Clear and enforceable regulations that promote PtX fuel adoption will be essential for building confidence among market stakeholders.
-
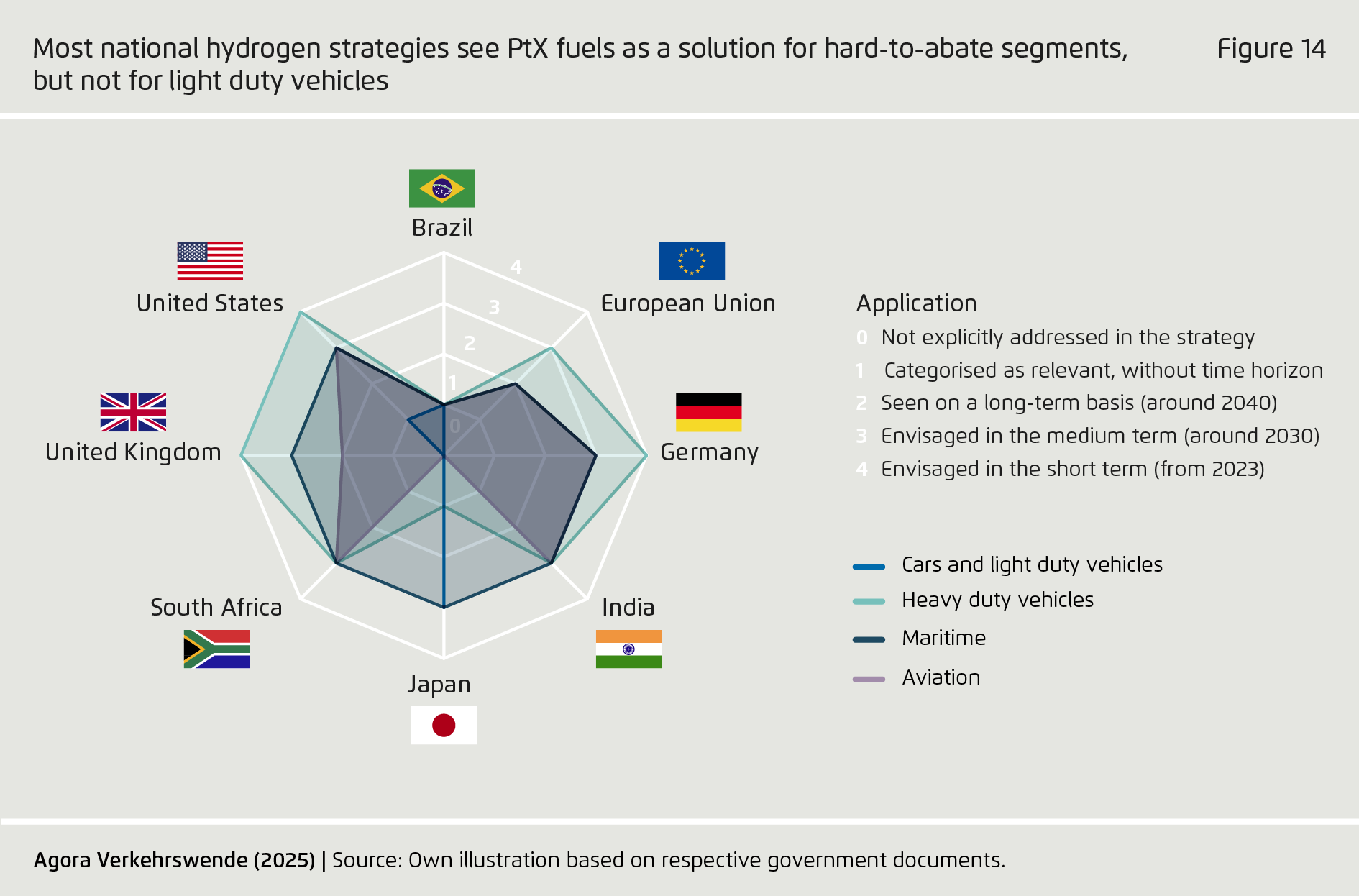
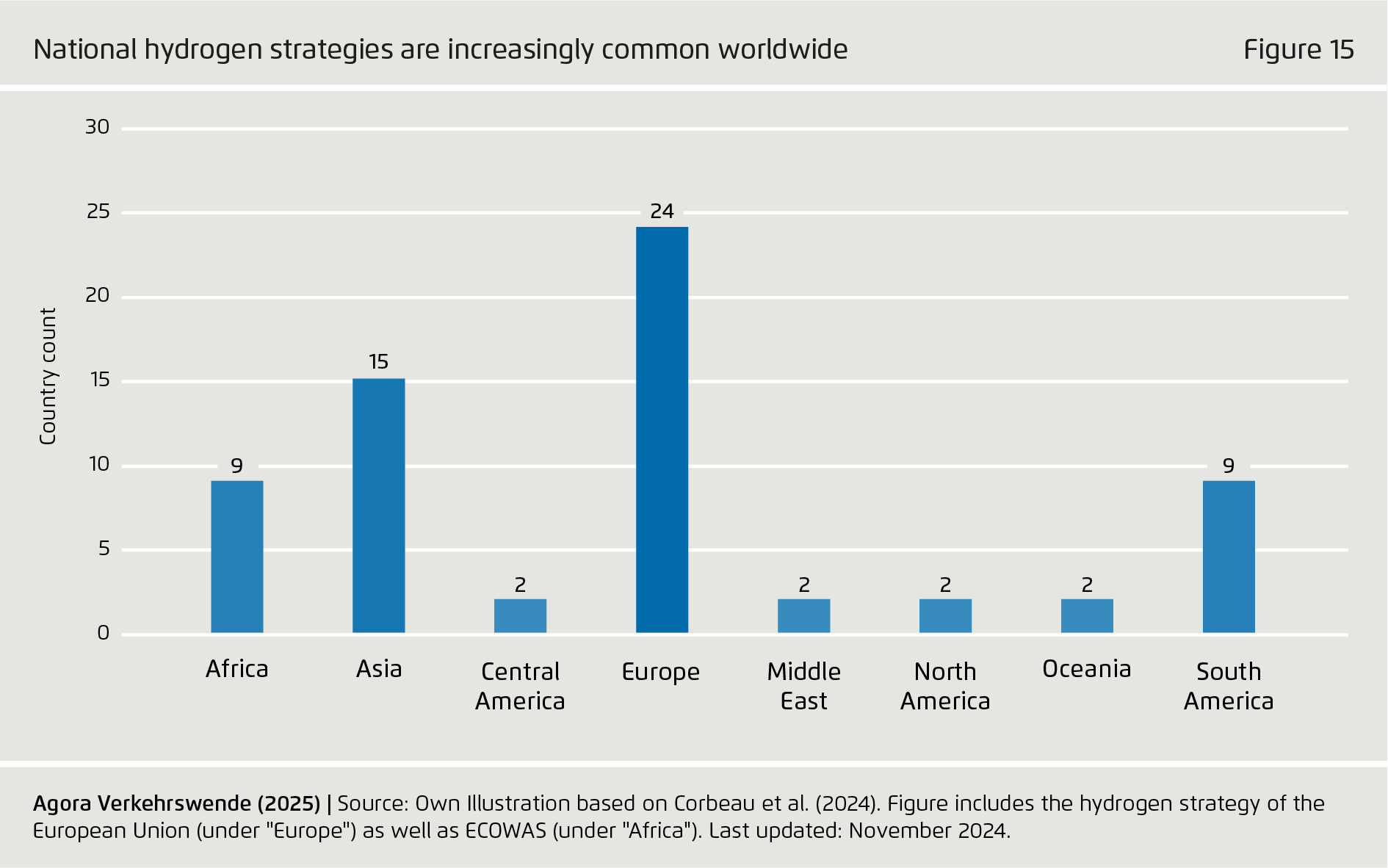
Policy ambition diverges considerably between countries.
While all eight jurisdictions considered in this report foresee PtX fuel adoption in transport, the EU, Germany and the UK have introduced the most ambitious and comprehensive policy regimes: In addition to a broader strategy for the hydrogen economy and sustainability standards, these jurisdictions have adopted binding regulatory measures (such as blending quotas) as well as market-based incentive measures (such as carbon pricing and auction schemes). While numerous policy initiatives have been launched in emerging economies, final implementation of “hard law” has been awaiting final implementation.
-
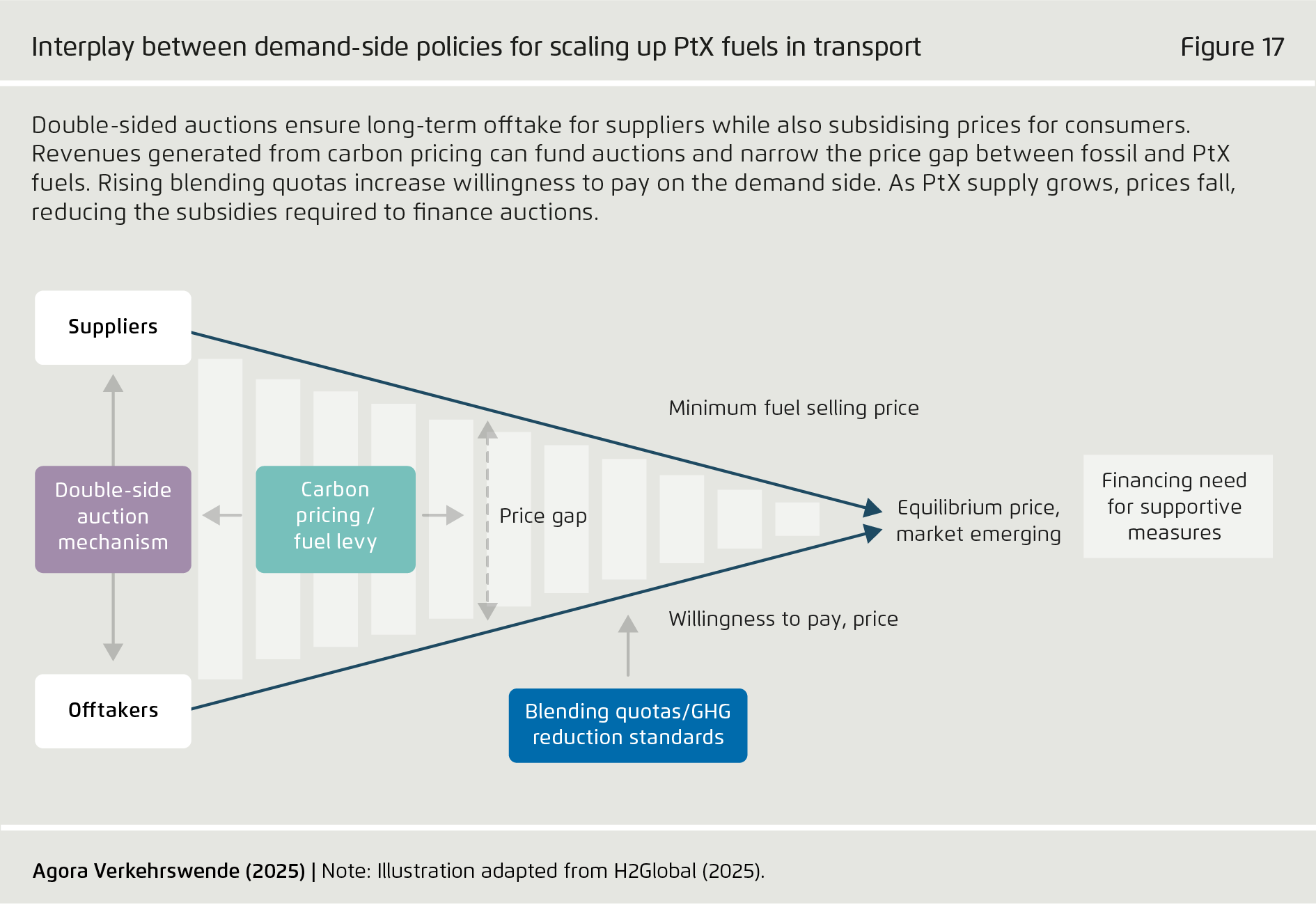
Successful PtX adoption in transport requires policies to stimulate supply and demand.
While quota schemes can create demand certainty by mandating PtX fuel blending at a fixed percentage, quotas by themselves are not enough to drive market ramp-up, as they fail to assure long-term price stability, which is essential for attracting large-scale investment. To address this problem, governments should implement market-based measures such as double-sided auction mechanisms. Double-sided auctions can provide producers with long-term offtake agreements and offtakers with PtX fuels at subsidized prices, thus ensuring reliable conditions for all market participants. These auctions can be funded with revenues from carbon pricing mechanisms or a dedicated levy on conventional fuels.
-
International collaboration is essential to align policies and unlock growth opportunities.
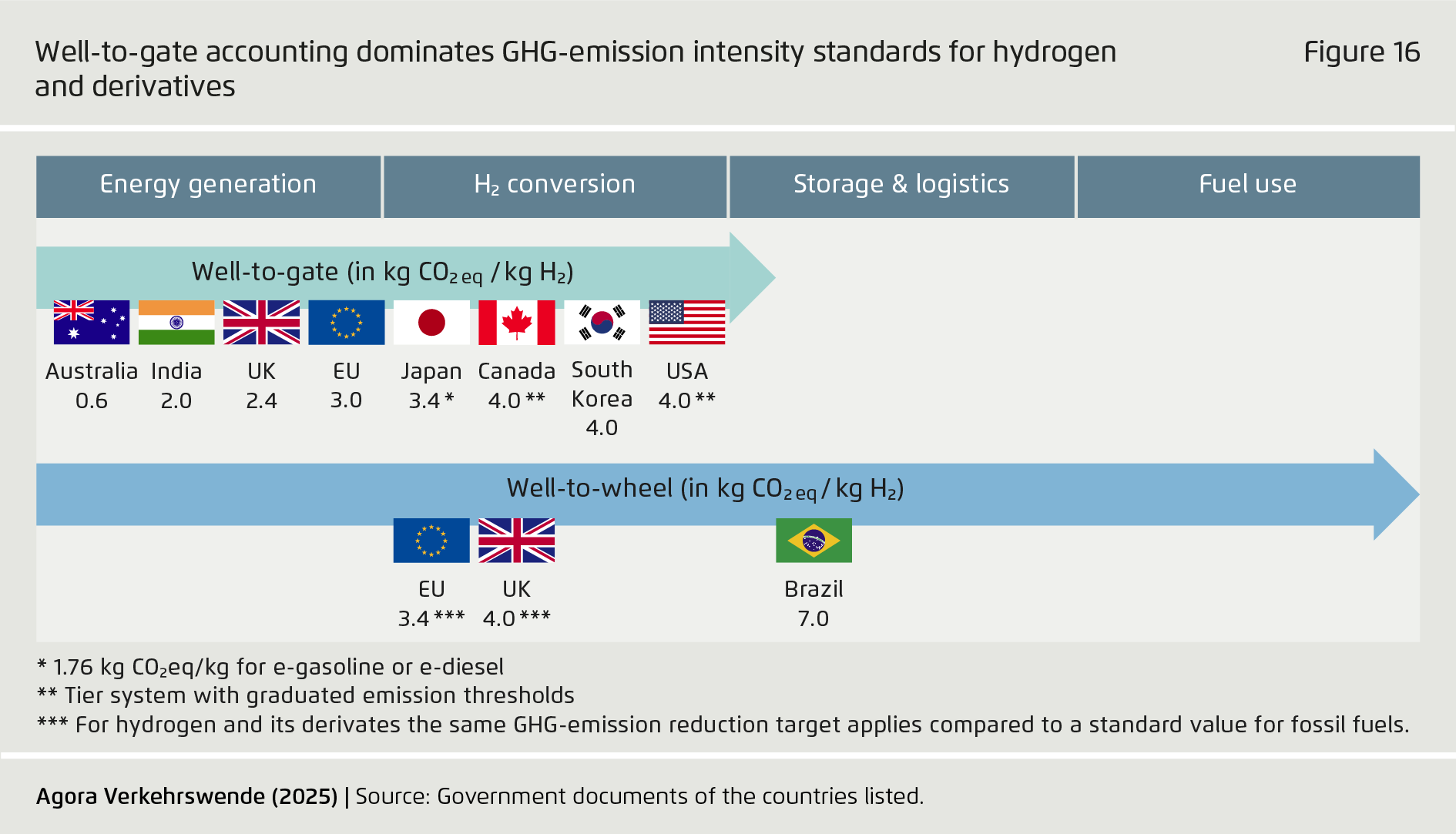
A successful global ramp-up will require harmonizing sustainability standards and implementing measures such as quotas and carbon pricing in a broad range of jurisdictions, in order to prevent carbon leakage. For emerging economies, international support will be key – not only for capacity building, but also for developing domestic value creation not geared solely to exports, thus ensuring broader economic benefits from PtX fuel adoption.
Scaling Power-to-X Fuels in Transport
A Cross-National Analysis and Policy Toolkit

Preface
Governments around the world have announced ambitious targets for the adoption of Power-to-X (PtX) fuels, and numerous production facilities are currently in planning. However, project developers continue to face significant hurdles in securing final investment decisions. This is a pressing concern, as the large-scale production of PtX fuels, including sustainable hydrogen and e-fuels, will be essential for achieving global climate neutrality – particularly in the hard-to-abate subsectors of international aviation and shipping.
PtX technology remains in the early stages of adoption. Accordingly, production has not yet taken place at the scale required to meaningfully contribute to defossilization in the hard-to-abate subsectors that lack electrification options. Against the backdrop of growing demand for transport, especially in emerging markets and developing economies, the deployment of PtX fuels must be urgently accelerated.
This discussion examines how targeted policies can effectively promote the uptake of PtX fuels in the transport sector. We consider both the challenges and opportunities that accompany policy development in this area, and, building on this analysis, propose a policy toolkit to support the PtX fuel economy. While our toolkit is applicable to all countries, we devote particular attention to the needs of emerging markets. Our goal is to inform both policymakers and stakeholders in the emerging PtX fuel economy about current policy trends and to contribute to the ongoing debate on how to effectively scale up these fuels, particularly in the transport sector.
Key findings
Bibliographical data
Downloads
-
Discussion Paper
pdf 2 MB
Scaling Power-to-X Fuels in Transport
A Cross-National Analysis and Policy Toolkit
-
Pressemitteilung
Globale Wasserstoff- und E-Fuel-Produktion für den Luft- und Seeverkehr ausbauen
Studie von Agora Verkehrswende zeigt, wie Regierungen strombasierte Kraftstoffe stärken können / Langsame Markteinführung gefährdet Klimaziele im Luft- und Seeverkehr / Mehr Tempo durch Quotenregelungen und staatlich geförderte Auktionen
All figures in this publication
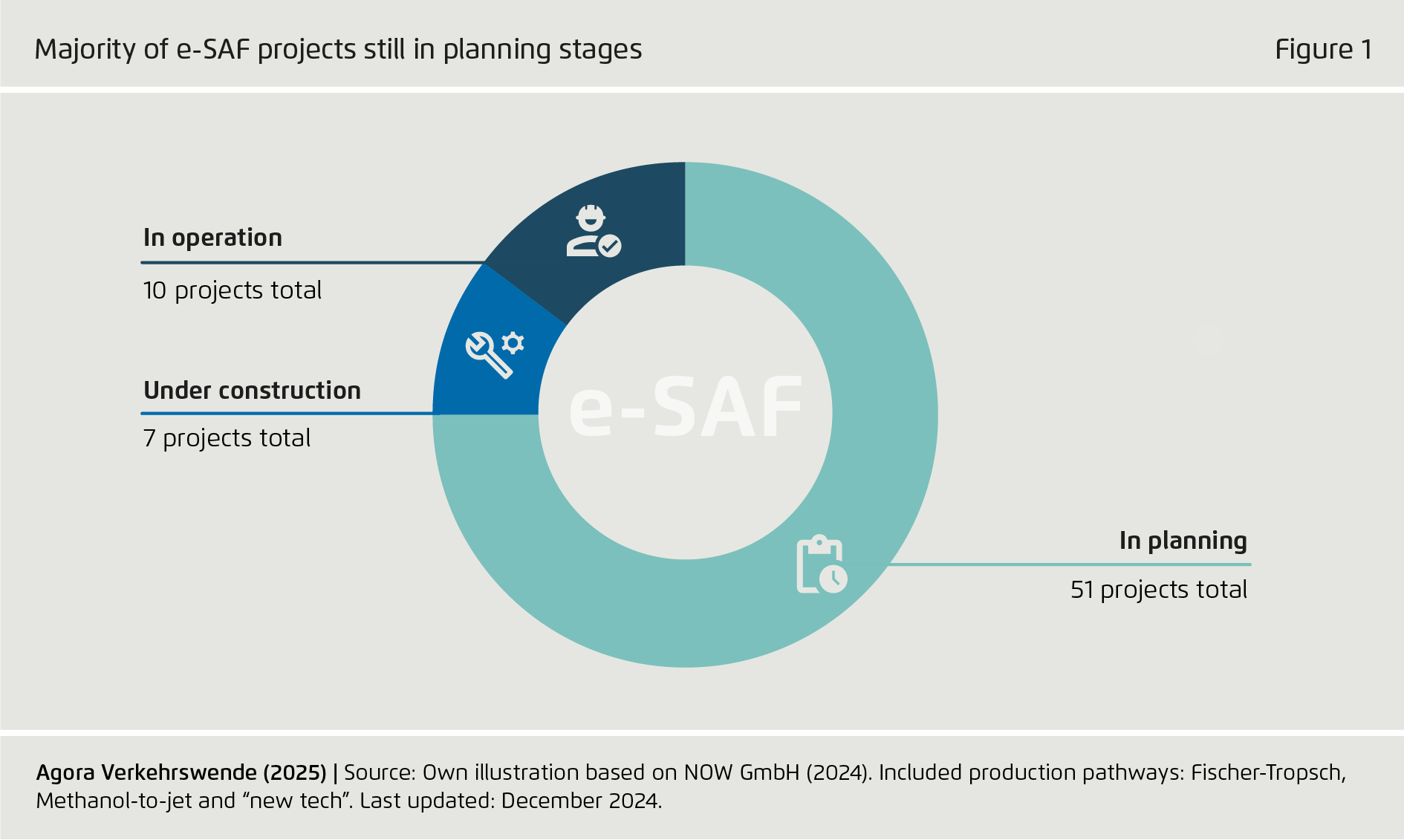
Majority of e-SAF projects still in planning stages
Figure 1 from Scaling Power-to-X Fuels in Transport on page 9
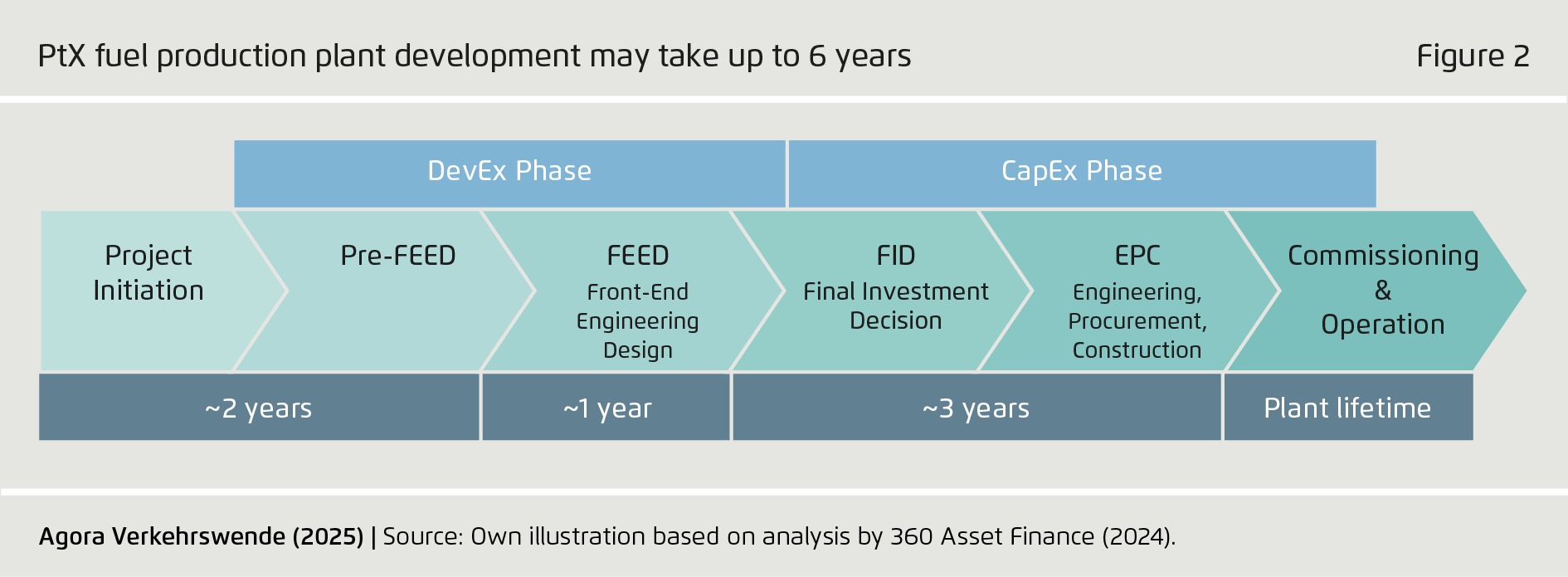
PtX fuel production plant development may take up to 6 years
Figure 2 from Scaling Power-to-X Fuels in Transport on page 10